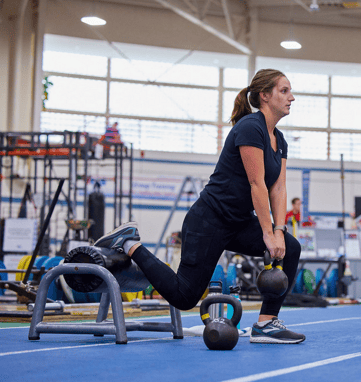 How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living.
How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living.
Activities of Daily Living
Your activities of daily living (ADLs) are your everyday activities that are essential to get you through the day: walking, getting up from chairs, carrying groceries, bringing in the bag of dog food, and so on. As a person ages, these activities get harder and harder to carry out. According to Harvard Health, it is estimated that after the age of 30, a person will begin to lose 3–5% of their muscle mass per decade. Loss of muscle mass will result in the loss of your ability to carry out your ADLs. Additionally, with loss of muscle comes the loss of muscular power, or the ability to produce force quickly. The loss of muscular power is the main contributor to the increase of fall risk as we age.
The loss of muscle mass as we age is termed sarcopenia. Age-related loss of muscle is, of course, preventable. With the correct diet, exercise plan, and regulation of hormones, a person can not only maintain but also increase their muscle mass as they age. This will ensure that you are able to maintain your ability to perform those ADLs with no trouble. Things such as yard work and playing outside with kids or grandkids are activities that should never be lost.
Athletics
Switching gears now to a different population. All aspects of strength are required to excel in a particular sport. From field sports to court sports to endurance running events, being strong will help everyone. The primary benefit that all athletes gain from strength training is an increase in joint stability. A well-structured resistance training plan will not only make the muscles stronger, but will also progress in a way to allow time to increase tendon strength at the same time. A more structurally sound joint is less likely to get injured.
Force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. Force is how we walk, jog, run, jump, change direction, and everything else we do in sport. There are two components that go into force, mass and acceleration. From a training aspect, we can manipulate these two components to match our needs. How this translates to the weight room is, we can move a light weight fast, or move as much weight as we can. Both forms of training will increase force production in their own way. Each athlete will need to train at different ends of the force curve depending on their sporting event and their biology. It is up to the strength and conditioning coach to make a plan for the individual’s needs and sport.
But I Don’t Want to Be “Bulky”
The common misconception is that resistance training will make you “bulky.” I only have one response to this question every time I get asked. I tell people to look at how track athletes and wrestlers train. These athletes are at peak performance but must maintain, and even in some cases lose, body weight. They do this by resistance training with very heavy loads for very low repetitions. This type of training increases muscular strength without increasing muscular hypertrophy (muscle size). If your goals are to increase strength and maintain your muscle mass, training with heavy loads and low volume is the route to take. This approach is also how powerlifters train. Their goal is to increase the amount they lift at a competition, but they must stay within their weight class. They cannot gain excess weight or else they will have to compete in a higher weight category.
The bodybuilders that you see at the very top level spend years and years building up their bodies to look the way they do. They train daily on individual muscle groups to sculpt their body to look perfect for the judges at a competition. Bodybuilders work in a higher-volume rep and set range than that of a strength athlete. Over an extended period of time, with the right diet, recovery habits, and in some cases the use of performance enhancers, bodybuilders are able to look the way they do when they step on stage. However, strength training two to four days a week to improve your health will not make you look like a “bulky” bodybuilder.
Strength Training Is for Everyone
Being strong is never a quality that someone wishes they did not have. A simple strength training regimen will not make you bulky, or weigh you down for everyday tasks. It will make you stronger and healthier. It will give you confidence to do new things, or things that you have been unable to do or wish you could do. Strength training will give you the ability to play with your kids, and then your grandkids after that in the same way. Not everyone wants to be a bodybuilder or a powerlifter, but everyone wants to feel good in their own skin. After all, nobody has ever complained about being too strong.

This blog was written by Evan James, NIFS Exercise Physiologist EP-C, Health Fitness Instructor, and Personal Trainer. To learn more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.



 I am often asked what is a good warm-up routine, and my answer typically consists of, “it depends.” A warm-up is typically done at the beginning of a training session and involves low-intensity movements to help get your body ready. The reason I tend to say “it depends” is that your goals, limitations, and what kind of training you have planned for a specific day will dictate your optimal warm-up.
I am often asked what is a good warm-up routine, and my answer typically consists of, “it depends.” A warm-up is typically done at the beginning of a training session and involves low-intensity movements to help get your body ready. The reason I tend to say “it depends” is that your goals, limitations, and what kind of training you have planned for a specific day will dictate your optimal warm-up.  VO2 max testing, or graded exercise testing, is a treadmill run or cycle to volitional fatigue—or pretty much going until you must stop. The test will tell us how many liters of oxygen you are able to take in and use for cellular respiration.
VO2 max testing, or graded exercise testing, is a treadmill run or cycle to volitional fatigue—or pretty much going until you must stop. The test will tell us how many liters of oxygen you are able to take in and use for cellular respiration. 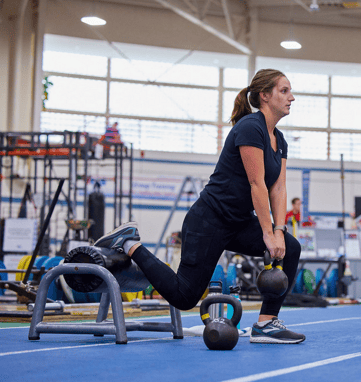 How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living.
How many times have you or someone you know needed help because they were unable to open the pickle jar? Now, how many times have you heard someone get mad because the pickle jar was too easy to open. I’m guessing you haven’t. Nobody has ever complained about being too strong—a statement I like to tell people when they ask why they should start strength training. There are many benefits of strength training. As we age we lose the physical ability to carry out certain activities. Tasks that were once easy are now difficult to do alone or not at all. These are our activities of daily living. 