 In my last blog, Impact of Exercise on Chronic Disease, I discussed. In this blog, I discuss COPD and how exercise can improve symptoms and quality of life for those affected. COPD is an acronym for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is an umbrella term defined by the CDC as, “a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems.” This is in contrast to some other pulmonary disorders that restrict lung expansion.
In my last blog, Impact of Exercise on Chronic Disease, I discussed. In this blog, I discuss COPD and how exercise can improve symptoms and quality of life for those affected. COPD is an acronym for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. It is an umbrella term defined by the CDC as, “a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems.” This is in contrast to some other pulmonary disorders that restrict lung expansion.
COPD is a global disease, but due to underreporting it is often overlooked. In developed countries it is often associated with smoking; however, its prevalence in many developing countries can be linked to outdoor, occupational, and indoor air pollution. Common symptoms include
- Shortness of breath at rest or with mild exertion
- Difficulty taking a deep breath
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Excess sputum production
Diagnosis and Treatment
Unlike many other health conditions, COPD is not diagnosed by a single test. Physicians often use a combination of medical history, imaging, and special breathing tests called pulmonary function tests to determine a diagnosis. Lower pulmonary function test scores indicate increased severity of COPD. Home treatment often includes medications such as bronchodilators, mucolytics, or supplemental oxygen. If you have COPD and plan on exercising, I recommend gathering your treatment information for your trainer so that they can determine any contraindications to exercise.
Counteracting the Downward Spiral
Because physical activity makes them short of breath, many individuals with COPD abstain from exercise. This sedentary behavior leads to increased health risks. Their heart becomes weaker, blood vessels are less flexible and more likely to rupture, and muscles atrophy from the lack of use. These physiological changes make it harder to perform physical activity and accelerate the downward spiral many people with this condition face. Because it is an irreversible disease, COPD cannot be cured with exercise. However, exercise can drastically improve the quality of life people experience.
How Exercise Helps People with COPD
The 2019 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Report states that exercise training can increase physical activity levels outside of the gym in COPD patients. It recommends that they participate in multiple brief bouts of high-intensity work. By doing so, these individuals can stress their cardiovascular system without putting it over the edge. Over time individuals with COPD experience similar cardiorespiratory adaptations to healthy populations, including
- Decreased blood pressure
- Decreased resting heart rate
- Increased blood flow to peripheral tissues
- Improved heart function
Resistance training also enables this population to complete activities of daily living more readily by increasing strength and muscular endurance. However, research shows that strength training does not improve their health status. A specific type of resistance training called inspiratory muscle training has been shown to increase the strength of inspiratory muscles, allowing individuals to take deeper breaths. Flexibility training is also believed to improve posture to allow for easier breathing, but no studies have specifically looked at this area.
NIFS Can Help
If you or somebody you know has COPD but doesn’t know where to start, speak with your physician about starting an exercise program. If cleared, come to NIFS, where we have trainers who are educated and certified to work with special populations. The Healthy Lifestyle Program is specifically designed to work with populations who need adaptations to exercise. If you are interested in joining the Healthy Lifestyle Program, stop on by and ask us what we can do for you!
This blog was written by Brandon Wind, ACSM Certified Exercise Physiologist. To find out more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 How do you define fitness? Whatever your answer is, it will shape the way you work out, influence the goals you set, and impact your long-term health. Although everyone might have different perceptions of what “fitness” means, the American College of Sports Medicine has defined what
How do you define fitness? Whatever your answer is, it will shape the way you work out, influence the goals you set, and impact your long-term health. Although everyone might have different perceptions of what “fitness” means, the American College of Sports Medicine has defined what  Think about the most recognized duos of all time: Batman and Robin. Mario and Luigi. Buzz and Woody. Stability and Mobility. Wait, what? Yes, like superhero teams, stability and mobility work together to achieve a balanced, harmonious environment for functional movement.
Think about the most recognized duos of all time: Batman and Robin. Mario and Luigi. Buzz and Woody. Stability and Mobility. Wait, what? Yes, like superhero teams, stability and mobility work together to achieve a balanced, harmonious environment for functional movement. When you hear the word stretch, you might think immediately about flexibility (or perhaps your lack thereof). Flexibility was always the term used for enhancing limited movement, until the word mobility arrived and took the fitness industry by storm.
When you hear the word stretch, you might think immediately about flexibility (or perhaps your lack thereof). Flexibility was always the term used for enhancing limited movement, until the word mobility arrived and took the fitness industry by storm. I know what you’re thinking: PiYo…sounds like some contortionist/new yoga trend, doesn’t it? Only for the truly flexible mind-body gurus, right? On the contrary, PiYo—our NIFS Group Fitness Class of the Month—has made its mark over the last 10 years in the fitness world, and its actual format just might surprise you.
I know what you’re thinking: PiYo…sounds like some contortionist/new yoga trend, doesn’t it? Only for the truly flexible mind-body gurus, right? On the contrary, PiYo—our NIFS Group Fitness Class of the Month—has made its mark over the last 10 years in the fitness world, and its actual format just might surprise you. Many of us know that yoga serves as a form of physical activity that increases flexibility for participants. Yoga focuses on putting the individuals in body poses that elongate muscles from head to toe. While this is very true, and I encourage anyone looking to improve their flexibility to incorporate yoga into their weekly workout routine, yoga has so much more to offer than just improvements in flexibility. In fact, the original context of yoga had very little to do with improving flexibility at all.
Many of us know that yoga serves as a form of physical activity that increases flexibility for participants. Yoga focuses on putting the individuals in body poses that elongate muscles from head to toe. While this is very true, and I encourage anyone looking to improve their flexibility to incorporate yoga into their weekly workout routine, yoga has so much more to offer than just improvements in flexibility. In fact, the original context of yoga had very little to do with improving flexibility at all. If you take a few minutes to google the various types of fitness training out there, you will come up with a list of about 10 different ones, and then 10 more different variations of each of those. And each year more and more “fitness trends” come out, making it quite confusing for the consumer as to what to choose and where to start. It can be confusing and even frustrating choosing what is right for you and your body.
If you take a few minutes to google the various types of fitness training out there, you will come up with a list of about 10 different ones, and then 10 more different variations of each of those. And each year more and more “fitness trends” come out, making it quite confusing for the consumer as to what to choose and where to start. It can be confusing and even frustrating choosing what is right for you and your body.  This type of training is specific to each individual and their personal zones. You can read more
This type of training is specific to each individual and their personal zones. You can read more 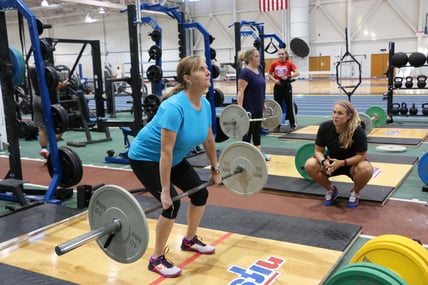 Strength training typically is done with heavy weight but can be done with lighter ones as well. This style of training is directly associated with Newton’s law: mass x acceleration = force.
Strength training typically is done with heavy weight but can be done with lighter ones as well. This style of training is directly associated with Newton’s law: mass x acceleration = force.  What Is Functional Training?
What Is Functional Training?
 We know it is encouraged by fitness professionals, and included at the end of group exercise classes, but I want to ask you, personally: how many times after a workout do you actually take the time to cool down?
We know it is encouraged by fitness professionals, and included at the end of group exercise classes, but I want to ask you, personally: how many times after a workout do you actually take the time to cool down?  Most of us might have been lucky to get out and play a handful of times over the winter, but some might be picking up a club for the first time in almost five months or more when that first tee time rolls around. Regardless of how many times you have played in recent months, everyone can benefit from improving golf-specific fitness areas before the full-fledged season begins.
Most of us might have been lucky to get out and play a handful of times over the winter, but some might be picking up a club for the first time in almost five months or more when that first tee time rolls around. Regardless of how many times you have played in recent months, everyone can benefit from improving golf-specific fitness areas before the full-fledged season begins. 