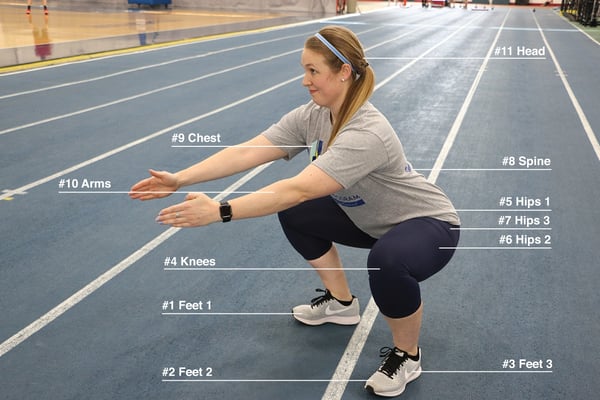
 If you’re like me and absolutely love listening to music and discovering new artists, genres, etc., then I could bet that you most likely listen to music while you exercise. Combining music and workouts has become a common practice among fitness enthusiasts because it can provide a boost of motivation and energy for when you’re testing your one-rep max or just taking a brisk walk outdoors. However, in this blog I will discuss the potential drawbacks of listening to music during a workout/training session and, hopefully, it will make you think about how music (or no music) plays a role in your training.
If you’re like me and absolutely love listening to music and discovering new artists, genres, etc., then I could bet that you most likely listen to music while you exercise. Combining music and workouts has become a common practice among fitness enthusiasts because it can provide a boost of motivation and energy for when you’re testing your one-rep max or just taking a brisk walk outdoors. However, in this blog I will discuss the potential drawbacks of listening to music during a workout/training session and, hopefully, it will make you think about how music (or no music) plays a role in your training.
Pros
Improved Athletic Performance
Music can help get you through some of your toughest workouts by improving your endurance and mentality and reducing perceived exertion. Finding the right playlist or song that fits with the intensity and tempo you plan to conquer will increase your chances of completing the exercise. (See some songs that NIFS trainers recommend here).
Mood Booster/Motivation
There’s nothing wrong with listening to your favorite workout jams to boost your mood and prep for a successful lift, run, or walk. In fact, listening to your favorite song(s) or playlist will improve your mentality going into the workout by significantly boosting both your motivation and confidence. Before I work out, I ALWAYS play my favorite songs to boost my mood and let my body know, “Hey, it’s almost time to work out and it’s time to get motivated!”
Decreased Chance of Fatigue
Listening to music improves your physical and mental endurance. Essentially, with music, you’ll most likely be able to lift more, run faster, and work harder. For example, say you’re doing a tempo run at a steady but challenging pace. Finding a playlist that matches your pace or cadence (steps per minute) will help you keep that mental toughness and complete the run.
Cons
Dependency
For some athletes (powerlifters, for example), listening to music during their big lifts may be beneficial for successfully completing the weight. However, if those athletes are training for a specific powerlifting meet that doesn’t allow the use of personal music or playlists, those athletes will most likely have a disadvantage. On the other hand, as a runner who completed a half marathon in May, I was able to use and rely on music to get me somewhat (still can’t believe I finished…wow) to the finish line. Overall, it depends on what you’re training for and the expectations of your game, meet, race, etc.
Decreased Athletic Performance
I know, yes, I did say music can aid in improving one’s athletic performance, but we must think about what kind of athlete we’re dealing with. For an Olympic lifter, powerlifter, or endurance athlete (runner, cyclist, etc.), music can be used without significantly disrupting their athletic performance. However, a gymnast or athlete training in calisthenics listening to fast-paced and upbeat music wouldn’t be ideal since their training relies on coordination, stability, focus, and balance.
Distraction (Technique, Safety, Form, etc.)
Music, especially if it's immersive, can divert your attention from maintaining proper form or technique. This distraction is risky when performing exercises that require precise movement patterns. It's essential to remain mindful of your body's alignment and ensure that music does not compromise your workout effectiveness or increase the risk of injury.
Overall Boredom
While music can be entertaining, it may not always be sufficient to combat boredom or monotony during long workout sessions. Relying solely on music for stimulation might not provide the variety and mental engagement needed to stay motivated over time. It's important to incorporate a mix of exercise routines and seek other sources of motivation to keep your workouts interesting.
The Bottom Line
Listening to music while working out can have numerous benefits, including increased motivation, enhanced performance, and improved mood. However, it's crucial to be mindful of potential safety concerns and avoid dependency on music. Finding a balance that suits your preferences, exercise goals, and safety considerations is key. Experiment with different approaches and find what works best for you to optimize your workout experience!
This blog was written by Deveon Martin, NIFS Health Fitness Specialist. To read more about the NIFS blogger, click here.


.jpg?width=532&height=342&name=GettyImages-1083005864(1).jpg) Muscle Mass Gains
Muscle Mass Gains
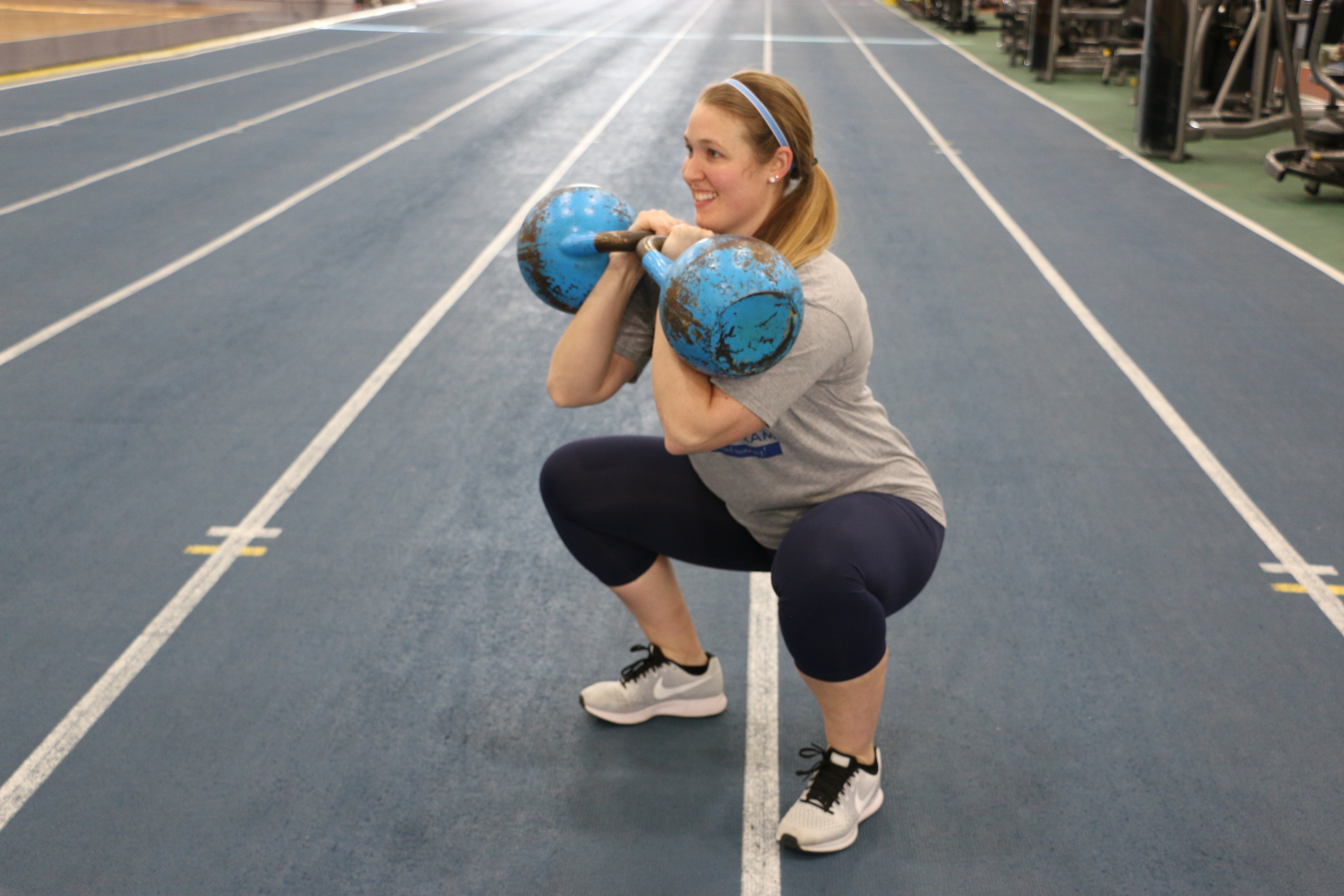
 With the sport of powerlifting taking off in the last couple of years, more and more people are taking up the sport as a hobby and to improve their overall fitness levels. Training to improve strength in the squat, bench, and deadlift is a great way to improve total body strength and improve body composition.
With the sport of powerlifting taking off in the last couple of years, more and more people are taking up the sport as a hobby and to improve their overall fitness levels. Training to improve strength in the squat, bench, and deadlift is a great way to improve total body strength and improve body composition. 

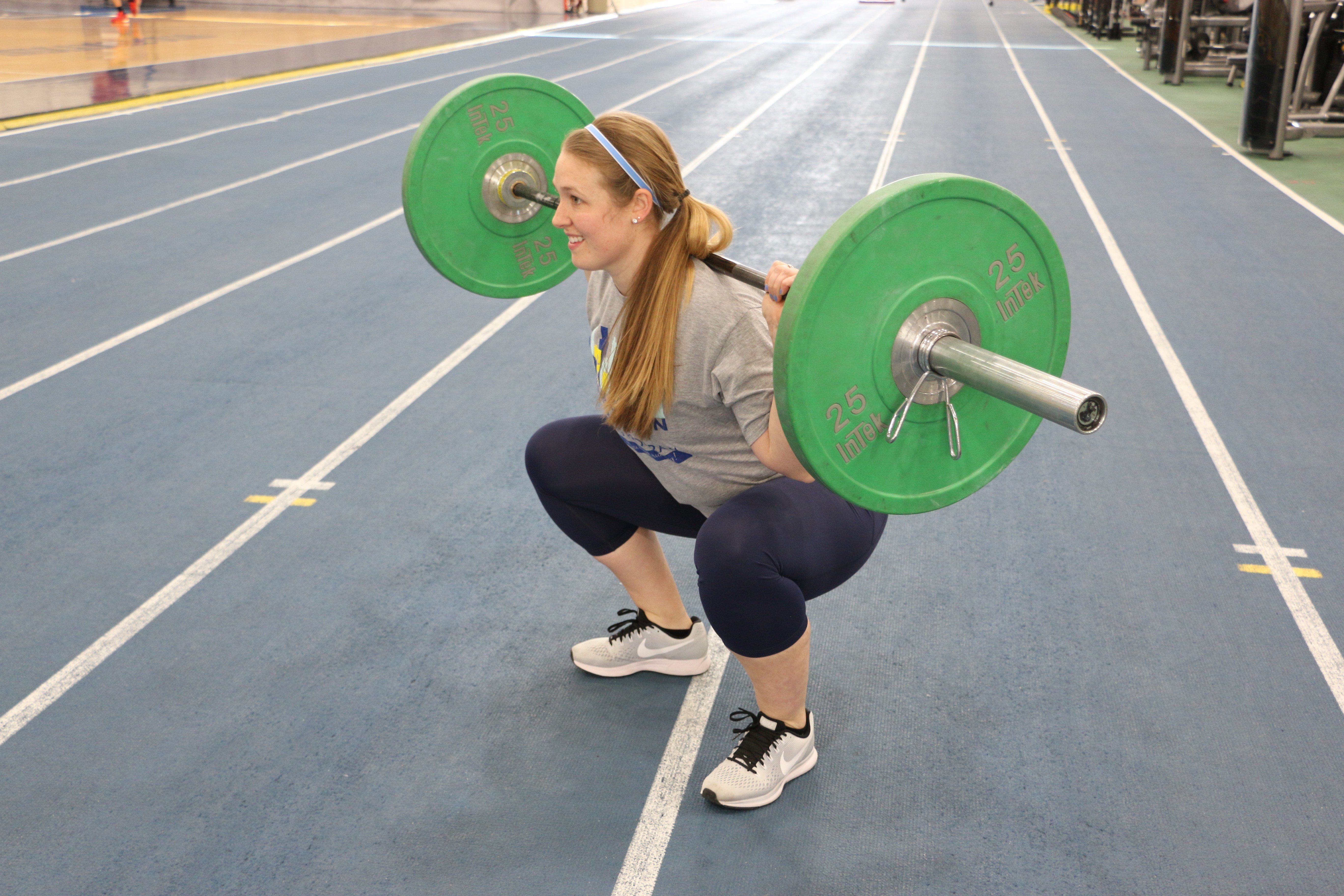
 Weight-lifting belts have become a staple in many gym settings for powerlifting, Olympic lifting, bodybuilding, and strongman, and for anyone who wants to lift heavy loads. Whether you use them for training or on the competition platform, you need to know the ins and outs of weight belts so that you can make a smart decision.
Weight-lifting belts have become a staple in many gym settings for powerlifting, Olympic lifting, bodybuilding, and strongman, and for anyone who wants to lift heavy loads. Whether you use them for training or on the competition platform, you need to know the ins and outs of weight belts so that you can make a smart decision. Over the last couple of years, I’ve noticed an increasing trend in bodybuilders and physique athletes migrating toward the sport of powerlifting. I’m no exception. I spent the first eight or so years of my lifting career focused almost exclusively on bodybuilding. Eventually, however, I got tired of the culture, the subjective judging criteria, and the politics involved in the sport. I decided that I’d rather be strong and functional rather than just big and muscular. Over the next couple of years, I began focusing more and more on strength-specific training. Eventually, this led me to my first NIFS Powerlifting Competition back in 2016.
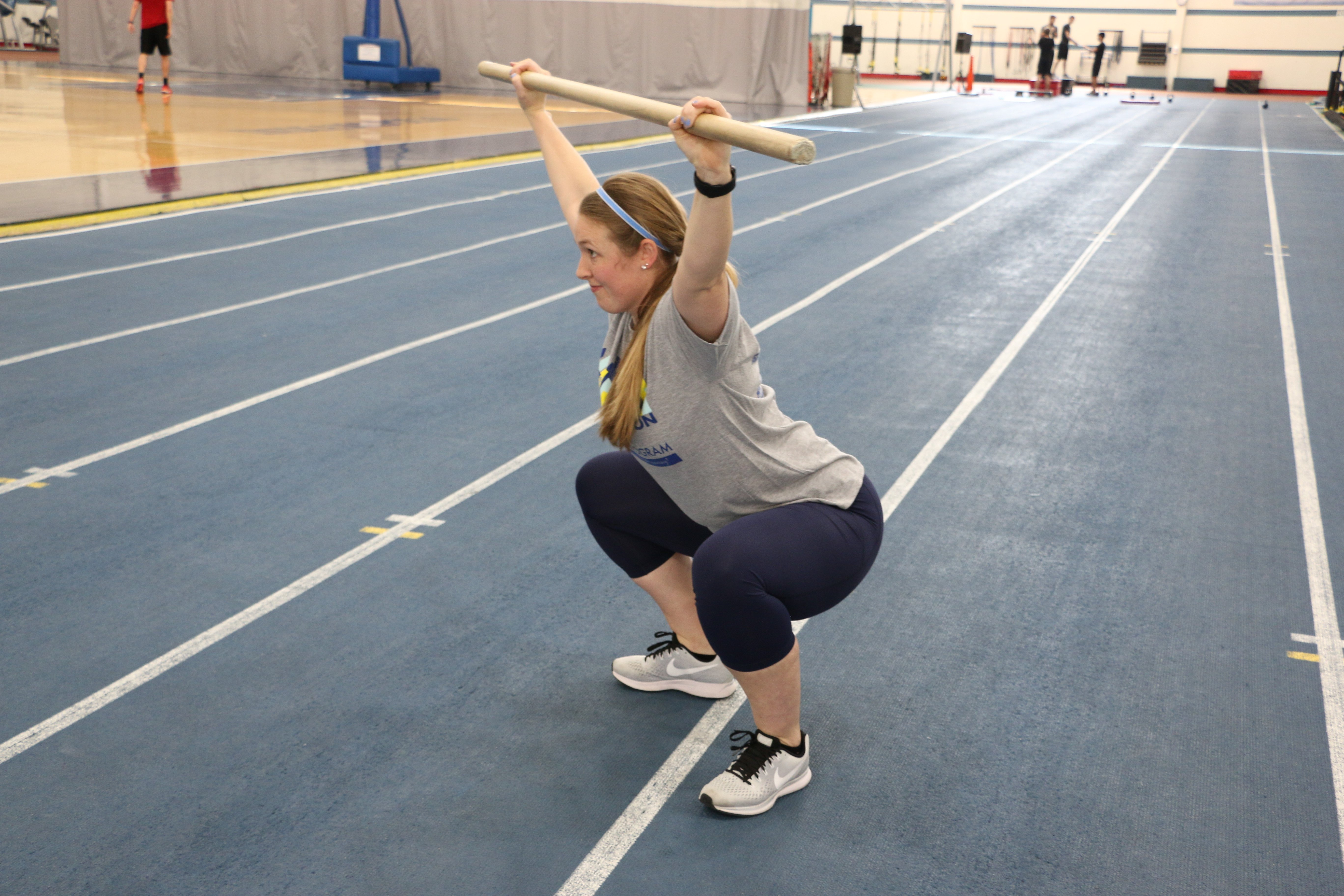
Over the last couple of years, I’ve noticed an increasing trend in bodybuilders and physique athletes migrating toward the sport of powerlifting. I’m no exception. I spent the first eight or so years of my lifting career focused almost exclusively on bodybuilding. Eventually, however, I got tired of the culture, the subjective judging criteria, and the politics involved in the sport. I decided that I’d rather be strong and functional rather than just big and muscular. Over the next couple of years, I began focusing more and more on strength-specific training. Eventually, this led me to my first NIFS Powerlifting Competition back in 2016. As a fitness professional I approach training and helping people from the direction that principles guide methods. The reason for this is that methods and fads will always change, but principles never do. It’s beneficial that the methods and variations of movements change from time to time, as long as the decision to change them is based on solid principles and reasoning. Variations are great, such as a change in foot position in a squat, adding load to a plank position, or varying the implement you are using during the exercise. One implement change that can pay heavy dividends (pun very much intended) is using a specialty lifting bar.
As a fitness professional I approach training and helping people from the direction that principles guide methods. The reason for this is that methods and fads will always change, but principles never do. It’s beneficial that the methods and variations of movements change from time to time, as long as the decision to change them is based on solid principles and reasoning. Variations are great, such as a change in foot position in a squat, adding load to a plank position, or varying the implement you are using during the exercise. One implement change that can pay heavy dividends (pun very much intended) is using a specialty lifting bar. Believe it or not, shoes do serve a higher purpose than just to make a fashion statement—especially when you’re
Believe it or not, shoes do serve a higher purpose than just to make a fashion statement—especially when you’re 


