 If you take a few minutes to google the various types of fitness training out there, you will come up with a list of about 10 different ones, and then 10 more different variations of each of those. And each year more and more “fitness trends” come out, making it quite confusing for the consumer as to what to choose and where to start. It can be confusing and even frustrating choosing what is right for you and your body.
If you take a few minutes to google the various types of fitness training out there, you will come up with a list of about 10 different ones, and then 10 more different variations of each of those. And each year more and more “fitness trends” come out, making it quite confusing for the consumer as to what to choose and where to start. It can be confusing and even frustrating choosing what is right for you and your body.
And to take it a step further, maybe the results you want that you aren’t getting are because you need to try something different. Maybe that different thing does not have to be some crazy, drastic change in gyms, your diet, or everything in your life. In fact, maybe it’s just a workout style that suits you better. Each product you see today—like CrossFit, Orangetheory, and Dailey Method to name a few—all follow a specific training method. And what works for one person doesn’t always work for the next.
I have narrowed it down to five categories of training methods, so let’s take a look at what each one is, and I’ll help you narrow down your focus.
Circuit Training
High intensity–style workouts that incorporate both aerobic exercise and strength training. These circuit workouts can be done with or without equipment.
- Target: Building strength and muscular endurance. These workouts tend to keep you on the higher end of your heart rate zones and are usually designed in stations for time, with little to no rest in-between.
- Goals: The circuit training method of exercise is good for those people who are looking for weight loss, are in a time crunch, or are looking for overall general fitness, a total-body workout, and toning. Many say this is where you get the most bang for your buck because you can get the results you are looking for in less time.
Aerobic Training
This type of training is generally summarized as meaning “with oxygen” or cardio training.
- Target: These workouts tend to target the cardiovascular system, mainly the heart and lungs. In most cases it’s associated with running, biking, swimming, jumprope, step class, and other cardio-based exercises. This style of training helps to increase your cardiovascular endurance and open the gap in your heart rate zones.
- Goals: The aerobic training style is good for those looking to lose weight, for specific training programs like marathons, for athletes looking to increase performance and endurance as well as recover appropriately, and for those trying to reduce the risk of chronic illness like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Heart Rate Training
 This type of training is specific to each individual and their personal zones. You can read more here about HR training, but this training method is focused in on zones like fat burn, cardiovascular endurance, peak performance, and recovery. In many cases, HR training is viewed as the all-around best training method there is.
This type of training is specific to each individual and their personal zones. You can read more here about HR training, but this training method is focused in on zones like fat burn, cardiovascular endurance, peak performance, and recovery. In many cases, HR training is viewed as the all-around best training method there is.
- Target: Heart rate training helps to increase endurance and sustainability in workouts by allowing you to peak and recover in a way that is specific to your body. Training zones are identified by doing a VO2 test.
- Goals: For anyone and everyone! Typically people training for endurance races like Spartans or marathons, or athletes honing in on max results and recovery, for the person who is totally burnt out after each workout, and all the way to people who are on medications that affect their heart rate.
Flexibility Training
Contrary to what I know everyone is thinking, it’s not just yoga! Forget the general stereotype of moms walking into the gym with lattes, flip-flops, and their yoga mat; this training style is probably the most important, yet the most neglected. It incorporates corrective exercises, stretching (both static and dynamic), and movements from head to toe.
- Target: To improve flexibility, mobility, range of motion, balance, and better posture.
- Goals: Another method of training that is for everyone! If you are not a yoga person, it’s time to start! Yoga folks, dancers, runners, meatheads: this is for you, too! Flexibility training is for every single person who wants to enhance their training in any way.
Strength Training
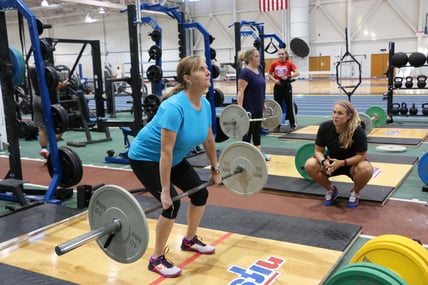 Strength training typically is done with heavy weight but can be done with lighter ones as well. This style of training is directly associated with Newton’s law: mass x acceleration = force.
Strength training typically is done with heavy weight but can be done with lighter ones as well. This style of training is directly associated with Newton’s law: mass x acceleration = force.
- Target: To increase muscle strength.
- Goals: Perfect for those looking to put on mass; can be good for those who don’t have a bunch of time to train; also good if you desire to move heavy things.
What should you do from here? If you are stuck in a rut or want to find the method that is going to be most effective for you, take some time to define your goals, figure out what is realistic for you, and take into consideration your past exercise experience. All these things play into what will work as well as what you like to do while in the gym.
This blog was written by Amanda Bireline, BS, CPT. To find out more about the NIFS bloggers, click here.


 It seems nearly impossible that the holidays have crept upon us already! And not just that, but those dreaded
It seems nearly impossible that the holidays have crept upon us already! And not just that, but those dreaded 
 Summertime is in full swing, and whether you are a competitive or recreational athlete, changes are definitely happening to your normal schedule. For high school and collegiate athletes, more time is spent at home and for general fitness enthusiasts, more options are available to you to fulfill your exercise quota (in other words,
Summertime is in full swing, and whether you are a competitive or recreational athlete, changes are definitely happening to your normal schedule. For high school and collegiate athletes, more time is spent at home and for general fitness enthusiasts, more options are available to you to fulfill your exercise quota (in other words,  What would life be without mistakes? It would be pretty boring, if you ask me. Making mistakes is the best way to learn. One mistake that most people have made is arriving at the gym and thinking, “What am I going to do here today?” I know I have done this plenty of times. When this happens, your motivation for your workout might decrease because you may just end up picking something that doesn’t really light a fire under you.
What would life be without mistakes? It would be pretty boring, if you ask me. Making mistakes is the best way to learn. One mistake that most people have made is arriving at the gym and thinking, “What am I going to do here today?” I know I have done this plenty of times. When this happens, your motivation for your workout might decrease because you may just end up picking something that doesn’t really light a fire under you.  For many triathlon participants, the swim is the most difficult discipline. Open-water swimming is different than following the black line on the bottom of a pool. Here are some tips to help the swim portion of the race go more smoothly.
For many triathlon participants, the swim is the most difficult discipline. Open-water swimming is different than following the black line on the bottom of a pool. Here are some tips to help the swim portion of the race go more smoothly.
 Over the past six to eights weeks, I have been creating summer workout manuals for the teams that I work with during the school year. These manuals are meant to bridge the strength and conditioning gap between the time they leave for summer break and when they return for the fall semester. There is much to be gained, or lost, through a summer of hard work (or lack thereof). Although summer break is a true “break” for most athletes academically, there never really is a true break for training.
Over the past six to eights weeks, I have been creating summer workout manuals for the teams that I work with during the school year. These manuals are meant to bridge the strength and conditioning gap between the time they leave for summer break and when they return for the fall semester. There is much to be gained, or lost, through a summer of hard work (or lack thereof). Although summer break is a true “break” for most athletes academically, there never really is a true break for training. Once the competitive season begins, scheduling time to get in to lift is a lot more difficult due to the practices, games, and travel that are happening. To me, in-season lifting is sometimes undervalued in the competitive/athletic world because of the fact that the primary focus is to win games or matches, not lift weights. However, I believe that this is one of the most important (if not the most important) times during the year because of what lifting can do for the athlete throughout the competitive season and into the off-season.
Once the competitive season begins, scheduling time to get in to lift is a lot more difficult due to the practices, games, and travel that are happening. To me, in-season lifting is sometimes undervalued in the competitive/athletic world because of the fact that the primary focus is to win games or matches, not lift weights. However, I believe that this is one of the most important (if not the most important) times during the year because of what lifting can do for the athlete throughout the competitive season and into the off-season. 
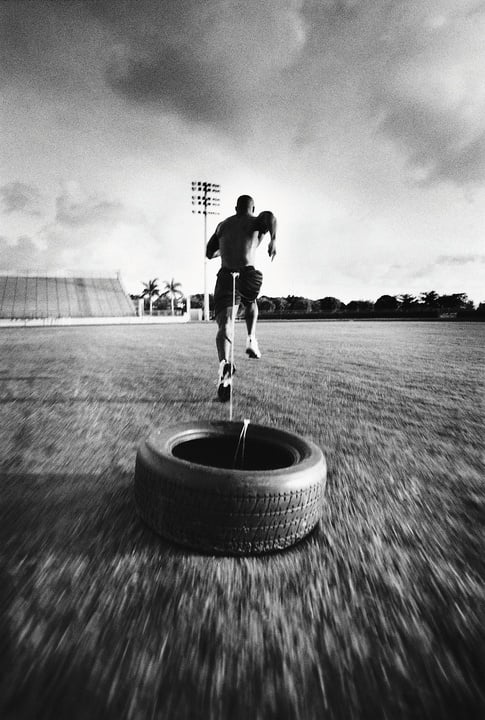


 When putting together a program for anyone, client or athlete, you always want to have an idea when you would like to peak, or be at your best throughout that calendar year. For
When putting together a program for anyone, client or athlete, you always want to have an idea when you would like to peak, or be at your best throughout that calendar year. For  In NFL and college football, each week, a star player is hit with a sidelining injury. Possibly lost for multiple weeks, months, or at worst, the whole season. Injuries that are usually the result of bad luck or not being as physically prepared as they could have been. Hopefully your team, **knock on wood**, does not or will not have to deal with this at any point during their season. My team, my beloved
In NFL and college football, each week, a star player is hit with a sidelining injury. Possibly lost for multiple weeks, months, or at worst, the whole season. Injuries that are usually the result of bad luck or not being as physically prepared as they could have been. Hopefully your team, **knock on wood**, does not or will not have to deal with this at any point during their season. My team, my beloved  As you can see, progression of strength (and power with other lifts) has to be maintained year round. This goes for all athletes throughout their seasons. If they want to continue to improve, they must prevent the loss. It is as important of a cycle of training as any. Without a properly structured in-season maintenance phase, you will be starting from the same place every time you start a new offseason training program.
As you can see, progression of strength (and power with other lifts) has to be maintained year round. This goes for all athletes throughout their seasons. If they want to continue to improve, they must prevent the loss. It is as important of a cycle of training as any. Without a properly structured in-season maintenance phase, you will be starting from the same place every time you start a new offseason training program.